

Cervical Cancer Screening Services for Women Living with HIV
This is part of the services being offered to women living with HIV from age 25-49 initially under the ACHIEVE Project and currently, ASPIRE project being implemented by EHAI in 3 LGAs in Nasarawa state as a sub-recipient to IHVN under CDC Nigeria.
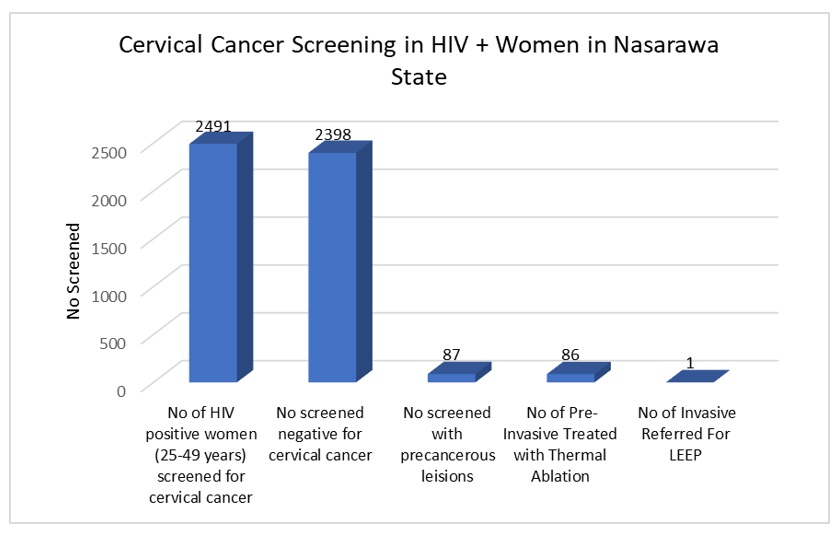
From 2020 till date, a total of 2491 women living with HIV have been screened through Visual Inspection (using Lugos Iodine or Acetic acid), out of which 87 clients (3.5%) had precancerous lesions and 86 of them were treated with thermal ablation. 1 person who had more than 75% lesion was referred to a tertiary facility for LEEP (Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure).
Evaluating the Impact of USAID TB LON 3 Domestic Resource Mobilization Project in Osun State, Southwest Nigeria (November 2020 – October 2022): In collaboration with Osun State TB and Leprosy Control Program and Osun State Health Insurance Agency (O-SHIA), EHAI is conducting a study aimed at evaluating the success of the USAID TB LON-3 Domestic Resource Mobilization Project in Osun State. The project is designed to improve Government funding for TB services as well as the integration of TB services into the Osun State Social Health Insurance Scheme (O-HIS). This repeated cross-sectional mixed method (qualitative and quantitative) study comprises of a baseline survey to obtain information on the level of Government Funding for TB services in the State as well as the state of TB intervention at the facility level and the experience of TB patients in accessing TB care and treatment services in Osun State prior to the intervention. The baseline survey will serve as a benchmark against which the results of the end line survey can be compared. An end of project evaluation will also be carried out using the same parameters and the result will be measured against the baseline survey to enable us obtain information on the success and impact of the intervention. On the survey, a validated and adapted Health Facility Assessment (HFA) and Patient Satisfaction Survey (PSS) tools will be applied to 72 health facilities (government, private for profit and private not-for-profit) and over 400 TB patients respectively for the quantitative arm of the survey. The quantitative aspect will entail conducting in-depth interviews with over 100 healthcare workers. The same survey tools will be utilized at the health facilities at the end-line survey. Computer Assisted Personal Interviewing (CAPI) tools will be utilized for the quantitative part of the survey (HFA and PSS) while all consent forms will be in hard copies.
Implementing an Urban Private Sector Model of IYCF Counselling in Private Health Facilities in Lagos State (6th March 2019 to 15th July 2020) Project: This IR project funded by the Alive&Thrive / FHI 360, was aimed at documenting the feasibility of implementing a standard package of Infant and Young Child Feeding (IYCF) counselling and support for pregnant women and mothers who use private health facilities in Lagos to improve Early Initiation of Breast Feeding (EIBF) and Exclusive Breast Feeding (EBF). This was a longitudinal cohort study, conducted in 10 intervention and 10 comparison Local Government Areas in Lagos. The goal was to measure the impact of implementing a standard package of Infant and Young Child Feeding (IYCF) counselling and support in private hospitals on breastfeeding practices among mothers in the intervention area versus those in the comparison areas in Lagos State. The primary objective was to measure differences in early breastfeeding initiation and exclusive breastfeeding among mothers in the A&T private provider intervention and comparison areas. While the secondary objectives were the measurement of differences in breastfeeding intentions among mothers in the A&T private provider intervention and comparison areas as well as assessment of the feasibility and acceptability of the intervention among private providers and mothers. During the survey, 600 women each in the intervention and comparison arm were interviewed during their 3rd trimester, within 30 days of delivery, and 5.5 months postpartum. There was also observations of client-provider interactions and client exit interviews as well as endline in-depth interviews with proprietors of private hospitals. EHAI was responsible for implementation of interventions and generation of data on the intervention arm of the project. On the intervention arm of the project, 2,350 Frontline healthcare workers and 1,685 Mothers & Women received behavioral change messages on early initiation of breastfeeding and exclusive breastfeeding via WhatsApp & SMS, while 5,323 pregnant women reached with similar messages across ANC clinics. Early initiation of breast feeding was successfully practiced in 72% of live births through the intervention and 65% of the children were reported to be on exclusive breastfeeding. Comprehensive report on the outcome of this study is yet to be released by the funders.
Baseline Assessment of Healthcare Quality and Human Resources for Health (HRH) Gap in Ekiti State (June 2017 – August 2017):
EHAI in collaboration with the Ekiti State Hospitals Management Board (HMB) developed a cross sectional needs assessment Research aimed at assessing the quality of healthcare delivery and human resources gap at government owned health facilities in Ekiti State focusing on the structures, processes and outcomes at the selected facilities. The study location was in selected Secondary Healthcare facilities picked based on simple random sampling. The study was designed to include a comprehensive desk review of the HRH structure in the state, administration of structured questionnaires and conducting interviews with key staff and patients from different units and departments in the hospitals with an adapted and validated needs assessment tool.
Operations Research (ACTION Plus Up Project): We are also involved in basic and operational scientific research to increase the body of knowledge as well as address key questions targeted at improving health outcomes, general well-being and providing innovative, cost efficient interventions and technologies. We have carried out several operations research including:
Several of our manuscripts are at different stages of review with international peer review journals. Some of our already published works include:
Effect of test- and -treat strategy on antiretroviral drugs uptake in a …
Assessing PMTCT service coverage in Southwest Nigeria: A step …www.gjmedph.com/uploads/O4-Vo5No1.pdf
Geriatric human immune deficiency virus (HIV) Infection in Nigeria
Impact of Repeated Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission of HIV …
Improving PMTCT Uptake and Quality of Care Through the Engagement of Traditional Birth Attendants (TBA) in Southern Nigeria – June 2015 – June 2016: This was a Global Fund supported Operations Research project funded by the National Agency for the Control of AIDS (NACA) through the West African Infectious Diseases Institute (WAIDI).
A cross sectional, mixed method (quantitative-qualitative) study, in which 1,200 questionnaires were administered and 6 focus group discussions (FGDs) with 18 key informant interviews (KIIs) were conducted in Southern Nigeria, across 3 LGAs in Edo, Enugu and Ogun states.
Recommendations were made in certain areas to strengthen TBAs so as to increase PMTCT uptake and quality of care TBAs render to their clients. Among these recommendations are training and capacity building for the TBAs, provision of materials and equipment such as HIV test kits, drugs etc. They also recommended that they be recognized by health facilities around them and there should be provision for a two way referral system between them and health facilities. Regular mentoring by relevant government organizations were also welcome and the TBAs are willing to co-manage their clients, HIV positive inclusive, with the orthodox health facilities. If TBAs are adequately engaged they can make a whole lot of difference in prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV in Nigeria.
Female Sex Workers and Access to HIV Counselling and Testing (HCT) and Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) Management Services in Lagos State South West Nigeria – June 2015 – June 2016: This was a Global Fund supported Operations Research project funded by the National Agency for the Control of AIDS (NACA) through the West African Infectious Diseases Institute (WAIDI).
It was a cross sectional mixed method (qualitative and quantitative) study aimed at exploring factors affecting the accessibility of FSWs to HCT and STI screening and treatment services and reviewing existing cluster model service delivery to FSWs. The study location was in three randomly selected Local Government Areas, one from each of the three senatorial districts in Lagos State: Agege (Lagos West), Apapa (Lagos Central) and Kosofe (Lagos East). 422 brothel and non-brothel based FSWs from randomly selected existing brothels and hotspots based on Level 1 and Level 2 Mapping and Characterization were recruited for the study through Peer Educators using a Stratified Purposive sampling method from the existing Highbrow (Apapa) and Lowbrow (Agege) brothels and hotspots LGA, Kosofe (Mixed).
Determining the Strongest Motivators for Acting on Routine Health Information in Family Planning – May 2016 – May 2017:
Background. Health system performance depends on the collection, collation, and use of quality health data and information. One of the primary roles of a routine health information system (RHIS) is generating data within the health system for decision making, policy formulation, and implementation. When data are generated and analyzed, they can provide relevant information to support planning and management of quality healthcare services at the facility, ward, local government, state, and federal levels. Stakeholders, including the government, can monitor performance and provide frameworks for guiding policies by which health services are provided. This study was conducted to bridge the knowledge gap concerning the motivators behind using routine health information (RHI) in family planning (FP) to improve the use of FP services.
Methods. The study design was a prospective cross-sectional study conducted over a period of 12 months in three local government areas of Lagos state in southwest Nigeria. Twelve key informant interviews (KIIs) were conducted and 425 questionnaires were administered to 105 men and 320 women working in the health sector.
Results: We found that nearly 90 percent of respondents are aware of RHI indicators in FP. The most common indicator (91.7%) is the number of injectables given. The most unfamiliar indicator (2.7%) is the number of referrals for FP services from prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV (PMTCT).
The biggest facilitators to using RHI in FP are:
abortion care (91.3%)
available
Virtually all respondents (99%) agreed on the importance of effective information technology infrastructure for data collection and use. More than 90 percent agreed that the biggest barriers to using routine FP data are poor-quality data and the lack of financial resources for supporting quality routine data collection.
A review of the current state of RHI in FP at organizations where respondents work shows incomplete availability of data-capturing tools (84%). Most documentation is done using paper-based collection tools, especially at public health facilities; some private health facilities use electronic medical records. Data storage, especially at the state agencies, is done using both paper-based and computer systems. None of the organizations have computer software for data analysis.
Recommendations. We strongly recommend the following: